Content Providers in Android
Posted By : Ajit Jati | 15-Jul-2013
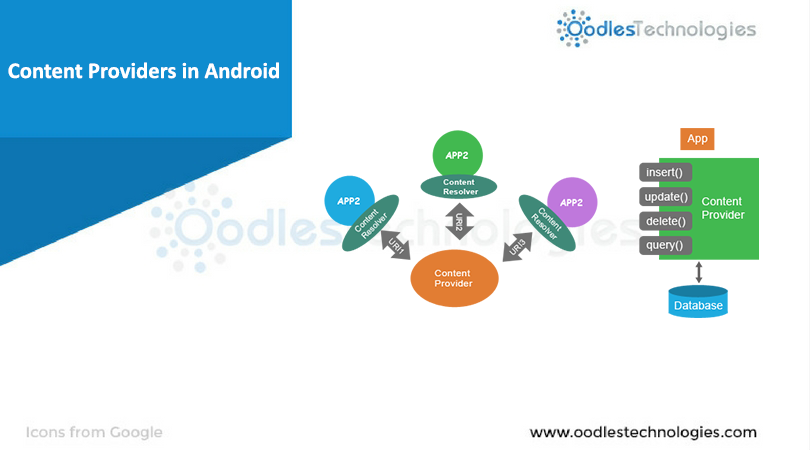
A database in Android System is private to the application which creates it. There is no common storage space in Android that multiple application can share. Therefore, for different applications to use a database, Android system needs an interface to have such inter-application data sharing. This is what content providers exactly do.Content Providers are used to share data between applications.
When you need a Content Provider ?
- If you want to create a database which will be private to your application(Which will not be shared with other applications) then you do not need a Content Provider.
- You will need a Custom content provider to be able to have a custom search suggestions in your own application system.
- You also need a Content Provider to move and use useful data from your app to other apps.
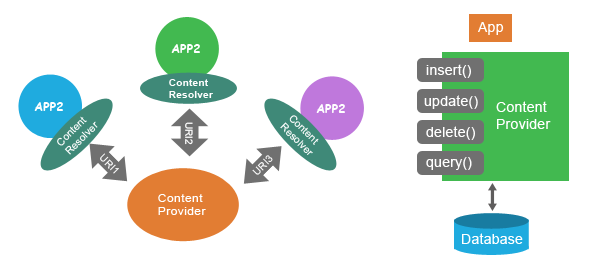
Some basic operations provided by Content provider are : Querying, insert, update, delete etc.Some default Content Providers Provided by Android OS are :
Contacts – Contact details
Call log – All call history
Media Store – Audio/Video details
Browser – Bookmarks, history, etc.
Settings – All phone settings like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Security, etc.
To create our own content provider we need to extend the ContentProvider class and override some methods defined within it.
In order to extract/manipulate data we mainly need two things:
- Uri
- Content Resolver object.
Uri
To get the data from an application we need Uri, the path where actual data is stored in a table. Example :
-to get contact details
content: //contacts/people
-to get bookmark details from browser
content: //browser/bookmarks
The general syntax for the URI is
<Standard prefix> ://< authority>/< data path>/<id>
In Android every content provider URI starts with
content://
if we want to get the 5th contact from the Contact list then the example would be :
content: //contacts/people/5
Content Resolver
To extract/get the data provided by the content provider’s we use content resolvers. The content resolver job is to dispatch our requests to a content provider, based on the given Uri. so whenever, we try to get data from ContentResolver, the system evaluates the given Uri and passes the request to theContentProvider. To get the content resolver object, we use getContentResolver() method within our application’s context.
ContentResolver resolver = getContentResolver();
The ContentResolver object provides the basic “RCUD” (Read,Create,Update and Delete) functions associated with the android storage.
Inorder to start with Content providers create a new project in android.
private String[] colummns = new String[]{
ContactsContract.Contacts._ID, ContactsContract.Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME, ContactsContract.Contacts.HAS_PHONE_NUMBER};
private Uri contactsListUri = ContactsContract.Contacts.CONTENT_URI;
private Uri phoneUri = ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.CONTENT_URI;
private String contactIdUri = ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.CONTACT_ID;
private String numberUri = ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.NUMBER;
private Cursor cursor;
private ArrayList<string> arrayList;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
arrayList = new ArrayList<string>();
cursor = managedQuery(contactsListUri, null, null, null,null);
readContacts();
}
void readContacts() {
if(cursor == null || cursor.getCount() == 0){
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "No Contacts in Your Directory", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
else{
while(cursor.moveToNext()){
String id = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(colummns[0]));
String name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(colummns[1]));
if(Integer.parseInt(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(colummns[2]))) > 0){
Cursor numCursor = managedQuery(phoneUri, null, contactIdUri + "=?", new String[] {id}, null);
if(numCursor.getCount()>0)
while(numCursor.moveToNext()){
String phone = numCursor.getString(numCursor.getColumnIndex(numberUri));
arrayList.add(name+"~"+phone);
}
}
}
getListView().setAdapter(new MyAdapter(arrayList,R.layout.namenumber,getLayoutInflater()));
}
}
}
Delete
To delete a row we use resolver.delete() method, which is having 3 parameters. Following is the syntax. rowDeleted = resolver.delete(Uri, selection, selectionArgs);
DeleteRecord.java
public class DeleteRecord extends ListActivity{
private String[] colummns = new String[]{
ContactsContract.Contacts._ID, ContactsContract.Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME, ContactsContract.Contacts.HAS_PHONE_NUMBER};
private Uri contactsListUri = ContactsContract.Contacts.CONTENT_URI;
private Uri phoneUri = ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.CONTENT_URI;
private String contactIdUri = ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.CONTACT_ID;
private String numberUri = ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.NUMBER;
private Cursor cursor;
private ArrayList<String> arrayList;
private String deleteName, deleteNum,deleteCombi;
private String[] splitCombi;
private AlertDialog.Builder builder;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
arrayList = new ArrayList<String>();
builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(DeleteRecord.this);
cursor = managedQuery(contactsListUri, null, null, null,null);
readContacts();
getListView().setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> arg0, View arg1, int arg2,
long arg3) {
deleteCombi = arrayList.get(arg2);
splitCombi = deleteCombi.split("~");
deleteName = splitCombi[0];
deleteNum = splitCombi[1];
builder.setTitle("Confirm");
builder.setMessage("Are You Sure to delete contact "+deleteName+"?");
builder.setPositiveButton("Yes", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
deleteContact();
finish();
startActivity(getIntent());
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Deleted Successfully", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
builder.setNegativeButton("No", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
builder.show();
}
});
}
private void deleteContact() {
Uri contactUri = Uri.withAppendedPath(PhoneLookup.CONTENT_FILTER_URI, Uri.encode(deleteNum));
Cursor cur = managedQuery(contactUri, null, null, null, null);
try{
if(cur.moveToNext()){
do{
if(cur.getString(cur.getColumnIndex(PhoneLookup.DISPLAY_NAME)).equals(deleteName)){
String key = cur.getString(cur.getColumnIndex(ContactsContract.Contacts.LOOKUP_KEY));
Uri uri = Uri.withAppendedPath(ContactsContract.Contacts.CONTENT_LOOKUP_URI, key);
getContentResolver().delete(uri, null, null);
}
}while(cur.moveToNext());
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Insert
ContentProviderOperation is used for performing batch operations. This class is useful for inserting a large number of rows or for inserting rows in multiple tables(batch operations).
InsertRecords.java
public class InsertARecord extends Activity{
private EditText name,number;
private Button buttonInsert;
private ArrayList<contentprovideroperation> operations;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.insertarecord);
operations = new ArrayList<contentprovideroperation>();
name = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.name);
number = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.number);
buttonInsert = (Button)findViewById(R.id.buttonInsert);
buttonInsert.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if(operations.size() > 0)
operations.clear();
operations.add(ContentProviderOperation.newInsert(ContactsContract.RawContacts.CONTENT_URI)
.withValue(ContactsContract.RawContacts.ACCOUNT_TYPE, null) .withValue(ContactsContract.RawContacts.ACCOUNT_NAME, null).build()); String displayName = name.getText().toString();
String phoneNumber = number.getText().toString();
if(!displayName.trim().equals("") && !phoneNumber.trim().equals("")){
operations.add(ContentProviderOperation.newInsert(ContactsContract.Data.CONTENT_URI)
.withValueBackReference(ContactsContract.Data.RAW_CONTACT_ID, 0)
.withValue(ContactsContract.Data.MIMETYPE, ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.StructuredName.CONTENT_ITEM_TYPE)
.withValue(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.StructuredName.DISPLAY_NAME, displayName).build());
operations.add(ContentProviderOperation.newInsert(ContactsContract.Data.CONTENT_URI)
.withValueBackReference(ContactsContract.Data.RAW_CONTACT_ID, 0)
.withValue(ContactsContract.Data.MIMETYPE, ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.CONTENT_ITEM_TYPE)
.withValue(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.NUMBER, phoneNumber)
.withValue(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.TYPE, ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.TYPE_MOBILE).build());
}
try{
getContentResolver().applyBatch(ContactsContract.AUTHORITY, operations);
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Insert Success", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
name.setText("");number.setText("");
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Insertion failed", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
});
}
}
public class UpdateRecord extends ListActivity{ private String[] colummns = new String[]{ ContactsContract.Contacts._ID, ContactsContract.Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME,ContactsContract.Contacts.HAS_PHONE_NUMBER}; private Uri contactsListUri = ContactsContract.Contacts.CONTENT_URI; private Uri phoneUri = ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.CONTENT_URI; private String contactIdUri = ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.CONTACT_ID; private String numberUri = ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.NUMBER; private Cursor cursor; private ArrayListarrayList; private String combi,b4Name,b4phNumber,upNumber; private String[] split; private Dialog dialog; private EditText eName, eNumber; private Button bUpdate, bCancel; private ArrayList ops; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); arrayList = new ArrayList (); dialog = new Dialog(this); dialog.setContentView(R.layout.update_dialog); eName = (EditText)dialog.findViewById(R.id.editName); eName.setKeyListener(null); eNumber = (EditText)dialog.findViewById(R.id.editNum); bUpdate = (Button)dialog.findViewById(R.id.update); bCancel = (Button)dialog.findViewById(R.id.cancel); bCancel.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { dialog.dismiss(); } }); bUpdate.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { upNumber = eNumber.getText().toString(); updateRecord(); finish(); startActivity(getIntent()); } }); cursor = managedQuery(contactsListUri, null, null, null,null); readContacts(); } protected void updateRecord() { Uri contactUri = Uri.withAppendedPath(PhoneLookup.CONTENT_FILTER_URI, Uri.encode(b4phNumber)); Cursor cur = managedQuery(contactUri, null, null, null, null); try{ if(cur.moveToNext()){ do{ if(cur.getString(cur.getColumnIndex(PhoneLookup.DISPLAY_NAME)).equals(b4Name)){ String id = cur.getString(cur.getColumnIndex(ContactsContract.Contacts._ID)); ops = new ArrayList (); String selection = Data.CONTACT_ID + "=? AND " + Data.MIMETYPE + " = '" + Phone.CONTENT_ITEM_TYPE + "' AND " + Phone.TYPE + "=?"; String[] selectionArgs = new String[]{id,String.valueOf(Phone.TYPE_MOBILE)}; ops.add(ContentProviderOperation.newUpdate(Data.CONTENT_URI) .withSelection(selection, selectionArgs) .withValue(Phone.NUMBER,upNumber).build()); getContentResolver().applyBatch(ContactsContract.AUTHORITY, ops); dialog.dismiss(); Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Update Success", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } }while(cur.moveToNext()); } }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Hope it helps understanding Content providers.
you can have a copy of the demo implementation using content providers to insert, modify, delete and read contacts within your Android phonebook.
cheers !! :)
Cookies are important to the proper functioning of a site. To improve your experience, we use cookies to remember log-in details and provide secure log-in, collect statistics to optimize site functionality, and deliver content tailored to your interests. Click Agree and Proceed to accept cookies and go directly to the site or click on View Cookie Settings to see detailed descriptions of the types of cookies and choose whether to accept certain cookies while on the site.










About Author
Ajit Jati
Ajit is an proficient Project Manager specializing in Mobile technologies. He possesses extensive development experience in Titanium, Android, Kotlin, Roku, and PHP. Ajit has successfully delivered various projects in the OTT, AR/VR, and Travel industries. His skill set includes developing and maintaining project plans, schedules, and budgets, ensuring timely delivery while staying within the allocated budget. He excels in collaborating closely with clients to define project scope and requirements, establish project timelines and milestones, and effectively manage expectations. He conducts regular project status meetings, ensuring effective communication and providing updates to clients and stakeholders on project progress, risks, and issues. Furthermore, Ajit takes on the role of a coach and mentor for team,offering guidance on project management best practices and assisting in their skill development.